As climate change continues its persistent advance, its main effects, such as higher temperatures and changes in rainfall patterns, are becoming increasingly frequent and clear. One such effect is the El Niño Phenomenon (ENP), an anomalous warming of the surface waters of the Central and Eastern Pacific Ocean, which, in turn, modifies the climatic conditions for South American Pacific coastal areas.
In the Andean countries (Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela), the relationship between climate change and the ENP can be seen in extreme weather variations. While torrential rains and floods ravage the coasts of Peru and Ecuador, severe droughts in the Andes mountains drastically reduce the availability of water. There have been three periods of particular exposure and impact—1982-1983, 1997-1998, and 2016-2017—categorized as episodes of extraordinary, strong and moderate magnitude, respectively. All of them have had significant socioeconomic impacts.
A recent IDB publication, “Effects of the El Niño Phenomenon in the Andean Region: An Empirical Approach,” published in Spanish, delves into this cyclical phenomenon, exploring how and to what extent the ENP affects the economies of the Andean countries. It focuses on changes in economic activity and price levels (inflation), two of the main macroeconomic indicators reflecting the regional economies’ welfare conditions. It also proposes measures to mitigate the ENP’s effects.
Figure 1. Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
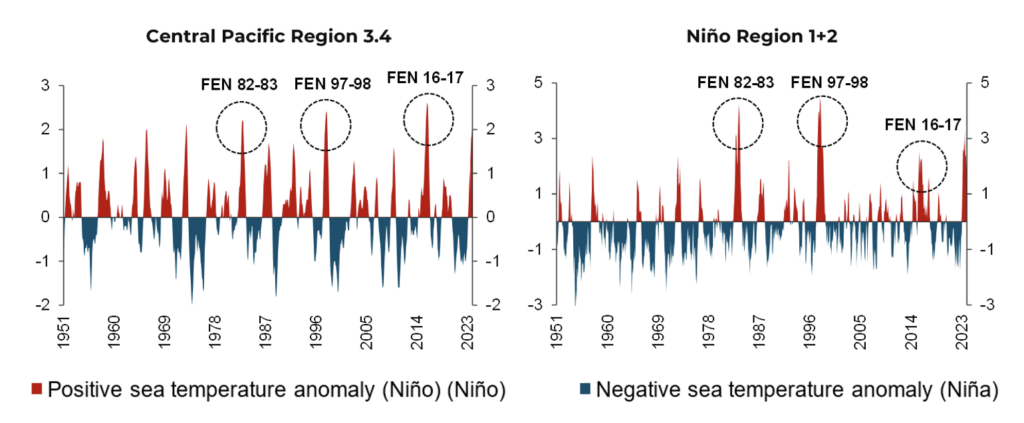
Note: Measures deviations from the average sea surface temperature in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific region. The study uses the Oceanic Niño Index (ONI) measured in a particular Pacific zone according to the country of interest. While for Peru it is Region 1+2, for the rest of the countries it is Central Region 3.4. FEN = El Niño Phenomenon (ENP).
The El Niño Phenomenon: A Cyclical Weather Event
These effects vary for every country in the Andes, with different weather phenomena and different intensities. And they deliver distinct impacts on economic sectors. In Bolivia, Ecuador, and Peru, for example, the ENP has caused excess precipitation, with significant effects on extractive activities such as fishing and agriculture. Meanwhile, in Colombia and Venezuela, it has generated a drop in rainfall, affecting the agricultural sector and electricity generation, with related increases in energy tariffs and inflationary pressure.
Figure 2. Economic Sectors most affected by El Niño
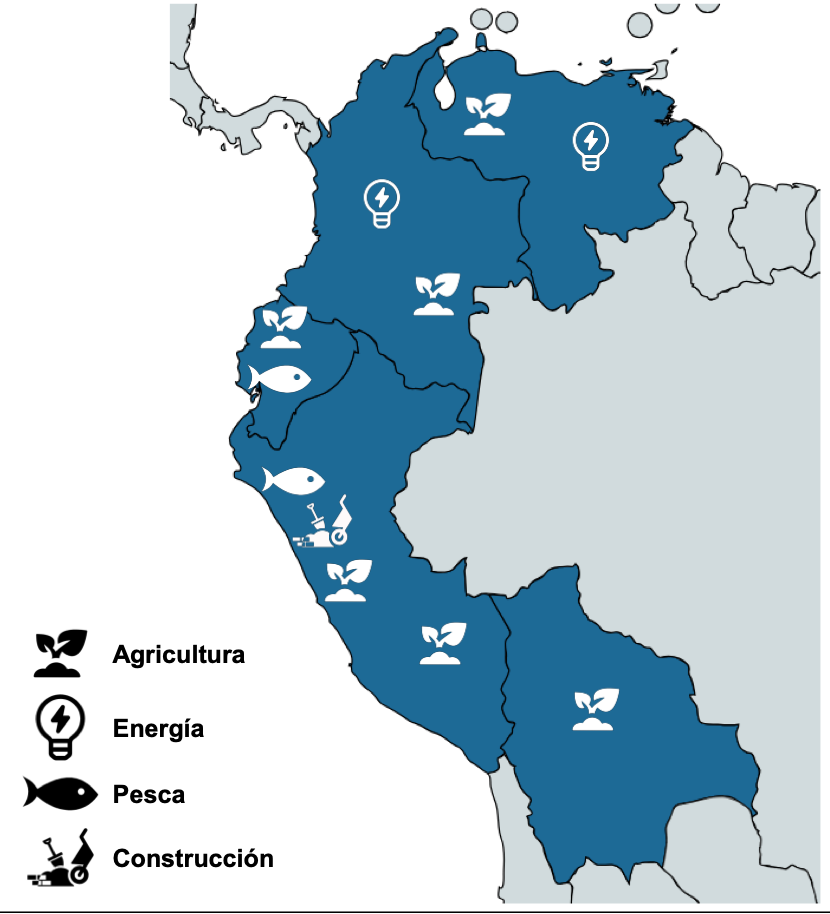
Note: Agricultura = Agriculture; Energia = Energy; Pesca = Fishing; Construcción = Construction.
The study analyzes these economic reactions to the ENP. It examines not only inflation but also economic growth in the face of different ENP magnitudes while comparing them to a baseline scenario in which the phenomenon did not occur. It also takes a historical perspective, analyzing what the economic impact of the ENP could have been in the recent 2023 event and, by extension, in future events of similar or greater magnitude, using past events as reference.
Deviations are estimated in percentage points with respect to a scenario in which there was no El Niño occurrence. The main results reveal that the ENP in the Andean region could have reduced economic growth in a range of 0.2 to 0.5 percentage points in the months of impact of 2023, and between 1.3 and 4.4 in the months of 2024, with Peru and Ecuador being the countries most susceptible to these impacts. A potential increase in inflation in Colombia and Peru of between 0.6 and 1.1 percentage points in 2023, and between 1.0 and 3.3 in 2024 was also found.
Figure 3. Economic Impact of the El Niño Phenomenon
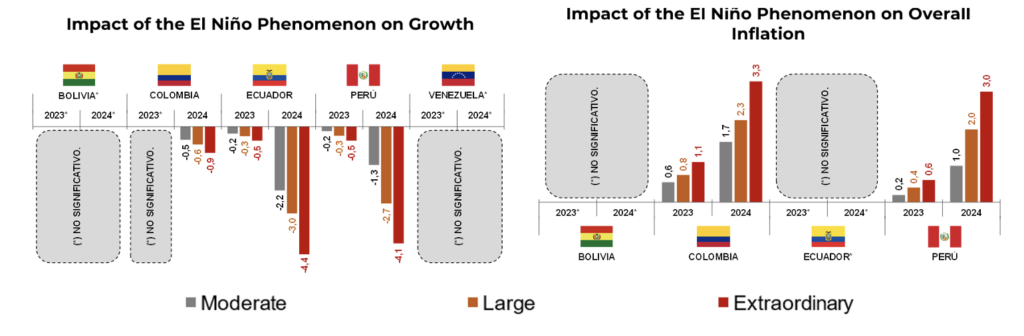
Note: The effect represents the difference of each ENP scenario with respect to a base scenario in which the non-occurrence of the phenomenon is assumed. No significativo = Not significant.
Lessons from El Niño’s Effects
These results suggest that, given the heterogeneous effects of the ENP in the Andean region, mitigation and adaptation strategies need to be implemented to counteract these effects at the economic and social levels. These could include infrastructure reconstruction, subsidies to affected sectors, and conditional transfers to cushion the transitory impacts of higher price levels on the region’s most vulnerable people. Flexible policymakers and adaptable economies will be crucial in the efforts to counteract the negative consequences of ENP-related extreme weather events and strengthen resilience as the adversities of climate change deepen.

1 Comment
Pingback: The Economic Impacts of Climate Change and El Niño in the Andes - TFFH - The Financial Freedom Hub