Subscribe to our YouTube channel for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Here we will learn how to rounding off to the nearest whole number?
Sometimes, we express approximate numbers instead of exact numbers. If someone says that there are 2000 students in a school, it does not mean that exactly 2000 students are there in the school. 2000 is the approximate number of students. It can be little more or little less.
If there are exactly 1991 or 2009 students, we usually say, there are 2000 students When we express a number to the nearest convenient number, which is easy to understand, is called Rounding off a number to a chosen place value.
While rounding off a whole number to a chosen place, we consider the next digit to the right of the chosen place. If this digit is 5 or more than 5, the digit at the chosen place is increased by 1 and all the digits to the right of the chosen place are replaced by zeros. If the digit to the right of the chosen place is less than 5, the digit at the chosen place remains the same and all the digits to the right side are replaced by zeros.
Let us consider some examples
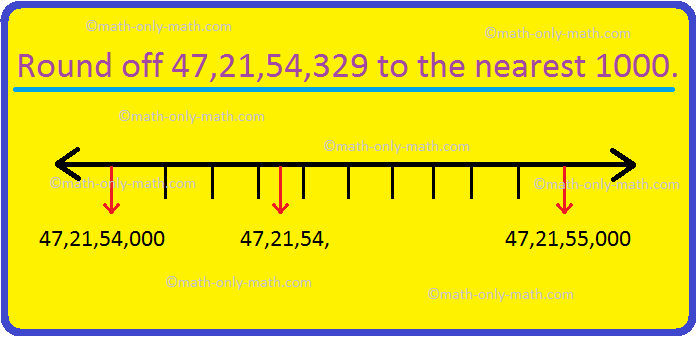
1. Round off 3667 to express it to the nearest thousands.
Solution:
We observe that the digit at hundreds place ie. 6 is greater than 5. So, we increase the digit at thousands place by 1 ie. 3 + 1 = 4 and replace the digits, at hundreds, tens and ones place by 0.
So, we can express the given number as 4000 to the nearest thousand
2. Round off 437 to express it to the nearest hundred.
Solution:
We observe that the digit of tens place ie. 3 is less than 5. So, the digit a
hundreds place remains the same le. 4 and the digits at tens and ones place are replaced by 0.
So, we can express the given number as 400 to its nearest hundred.
I: Rounding off a Number to the Nearest Ten:
(i) When the ones digit is 5 or more than 5, increase the tens digit by 1 and replace the ones digit by 0.
For example, 38 can be rounded off as 40 to the nearest ten. Here, ones digit is 8 which is more than 5. So, we replace 3 by 4 and 8 by 0.
(ii) When ones digit is less than 5, we replace the ones digit by 0. The tens digit remains the same.
For example, 32 can be rounded off as 30 to the nearest ten. Here, ones digit is 2 which is less than 5. So, we replace 2 by 0 and 3 remains the same. Let us consider some examples.
1. Round off the following numbers to the nearest ten.
(α) 47
(b) 82
Solution:
(a) We consider the digit at ones place.
So, 47 can be rounded off to the nearest ten as 50.
(b) We consider the digit at ones place.
So, 82 can be rounded off to the nearest ten as 80.
2. Round off the following numbers to the nearest ten.
(α) 457
(b) 394
Solution:
(a) In 457, the digits at ones place is 7.
7 > 5
So, 457 can be rounded off to the nearest ten as 460.
(b) In 394, the digit at ones place is 4.
4
So, 394 can be rounded off to the nearest ten as 390.
II: Rounding off a Number to the Nearest Hundred:
(i) When the tens digit is 5 or more than 5, we replace the ones and tens digits by 0 and increase the hundreds digit by 1.
For example, 362 can be rounded off as 400 to the nearest hundred. (tens digit i.e., 6 > 5)
(ii) When the tens digit is less than 5, we replace the ones and tens digits by 0. The hundreds digit remains the same
For example, 447 can be rounded off as 400 to the nearest hundred. (tens digit i.e., 4
Let us consider some examples.
1. Round off the following numbers to the nearest hundred.
(α) 893
(b) 345
Solution:
(a) In 893, the digits at tens place is 9.
So, 893 can be rounded off to the nearest hundred as 900.
(b) In 345, the digits at tens place is 4.
4
So, 345 can be rounded off to the nearest hundred as 300.
2. Round off the following numbers to the nearest hundred.
(i) 856
(ii) 720
Solution:
(i) In 856, the digits at tens place is 5.
So, 856 can be rounded off to the nearest hundred as 900.
(ii) In 720, the digits at tens place is 2.
2
So, 720 can be rounded off to the nearest hundred as 700.
III: Rounding off a Number to the Nearest Thousand:
(i) When the hundreds digit is 5 or more than 5, we replace ones, tens and hundreds digit by 0 and increase the thousands digit by 1.
For example, 2633 can be rounded off as 3000 to the nearest thousand. (6 > 5)
(ii) When the hundreds digit is less than 5, we replace ones, tens and hundreds digits by 0. The thousands digit remains the same.
For example, 2389 can be rounded off as 2000 to the nearest thousand. (3
Let us consider an example.
1. Round off the following numbers to the nearest thousand.
(α) 8614
(b) 7429
Solution:
(a) In 8614, the digit at hundreds place is 6.
6 > 5
So, 8614 can be rounded off to the nearest thousand as 9000.
(b) In 7429, the digit at hundreds place is 4.
4
So, 7429 can be rounded off to the nearest thousand as 7000.
Let us round off some larger numbers.
2. Round off the following numbers to the nearest ten thousand.
(a) 62125
(b) 86098
Solution:
(a) In 62125, the thousands digit is 2
2
So, 62125 can be rounded off as 60000 to the nearest thousand.
(b) In 86098, the thousands digit is 6.
6 > 5
So, 86098 can be rounded off as 90000.
2. Round off the following numbers to the nearest ten-lakh.
(a) 52436221
(b) 18764599
Solution:
(a) In 52436221, the lakhs digit is 4.
4
So, 52436221 can be rounded off to the nearest ten-lakh as 52000000.
(b) In 18764599, the lakhs digit is 7.
7 > 5
So, 18764599 can be rounded off to the nearest ten-lakh as 19000000.
Note: Following the above pattern, we can round off the numbers to the nearest crore and ten-crore also.
5th Grade Numbers Page
5th Grade Math Problems
5th Grade Math Worksheets
From Rounding Off to the Nearest Whole Number to HOME PAGE
Didn’t find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information
about Math Only Math.
Use this Google Search to find what you need.